Blockchain and Data Integrity in Computer System Validation

Blockchain was created in 1991 but it became known only in 2009 with Bitcoin. It aimed to be a viable alternative to financial relations that could be made directly between people, without the need for a trust institution, as a bank. Today, it is considered a technology capable of changing the whole system of economic activity and industrial.
Cryptocurrencies are a reward for people who are part of this network by 'mining' special codes to validate financial transactions between users.
But the possibilities of using Blockchain technology are many and companies are investing to acquire the transparency and security that the technology offers to the supply chain.
From data storage and security point of view in the Life Sciences industries, Blockchain technology offers 3 essential conditions to ensure data integrity: security, action traceability and transparency in data handling.
Currently, relevant GxP data (data that impacts in Good Practices) is stored in databases, which undergoes through validation to ensure its integrity according to regulatory agency standards. And in a structure with Blockchain technology, how would this data be treated?
But the possibilities of using Blockchain technology are many and companies are investing to acquire the transparency and security that the technology offers to the supply chain.
From data storage and security point of view in the Life Sciences industries, Blockchain technology offers 3 essential conditions to ensure data integrity: security, action traceability and transparency in data handling.
Currently, relevant GxP data (data that impacts in Good Practices) is stored in databases, which undergoes through validation to ensure its integrity according to regulatory agency standards. And in a structure with Blockchain technology, how would this data be treated?
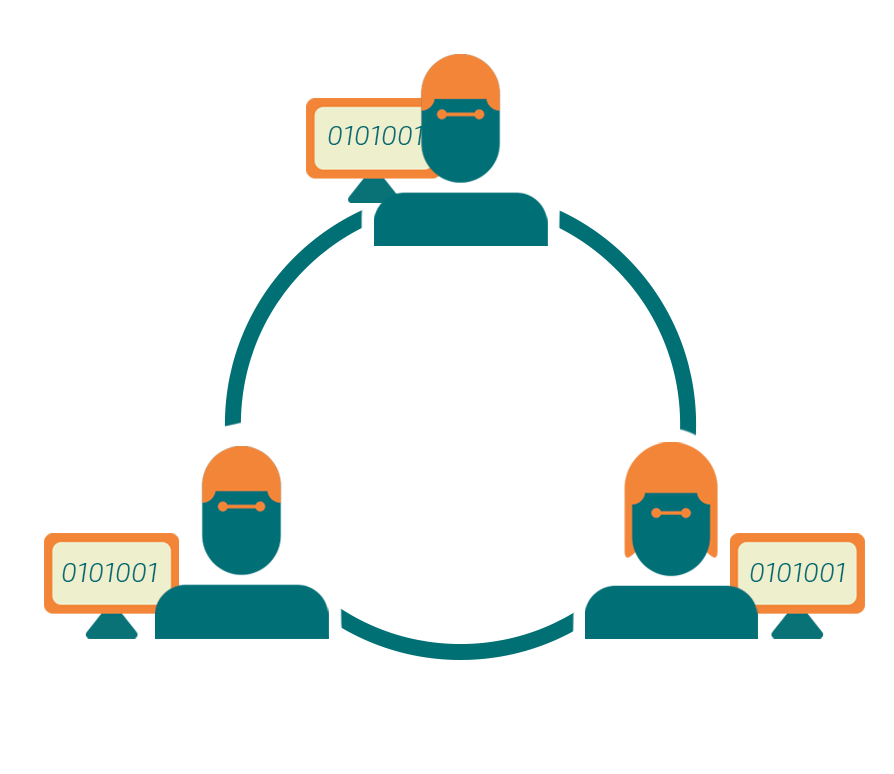
Blockchain technologies that ensure security of stored data
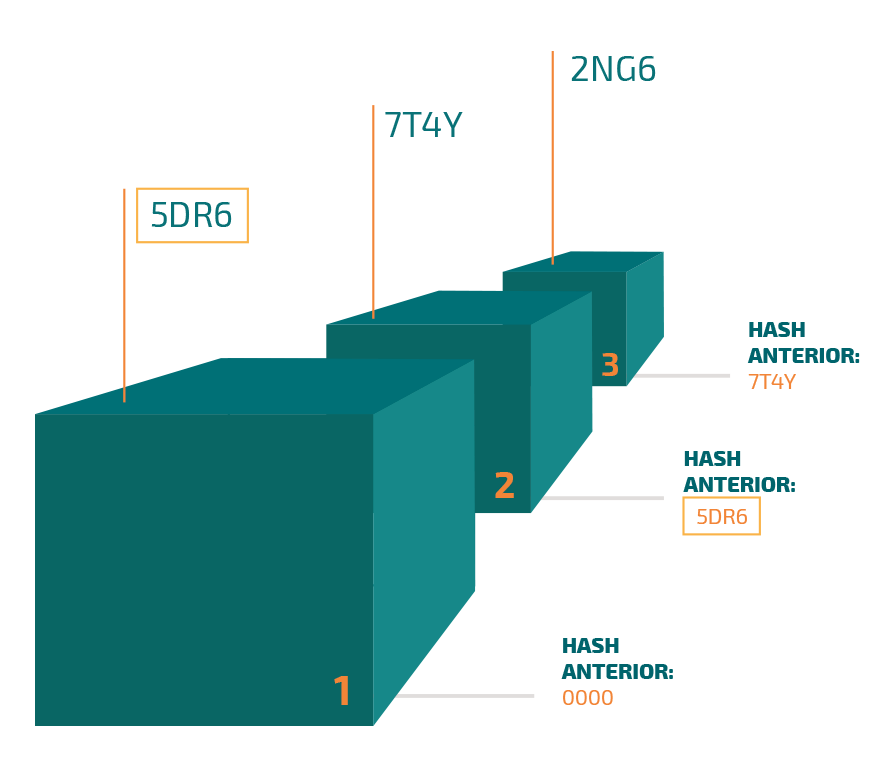
Hash identification and data divided into blocks
When data from the supply chain is inserted into a structure based on Blockchain technology, that data is divided into blocks and these blocks are distributed in different devices that participate in this production chain.
Each block of this data contains, in addition to the production data, a unique identification called the 'Hash' and the 'Hash' of the block before it, which identifies another part of this same GxP data.
The blockchain of a data is then formed by this 'hash' identification of the block itself and the block prior to it.
When any unauthorized alteration or attempted manipulation occurs in one of the blocks in this chain, the Hash number is changed. Consequently, all points in this network that have access to these transactions will cause inconsistency of the improper alteration and it will not validate this new information entered.
If the data entered is not validated, it will not be part of this block chain causing hash tag non-receipt needed to link it to the other data blocks.
When data from the supply chain is inserted into a structure based on Blockchain technology, that data is divided into blocks and these blocks are distributed in different devices that participate in this production chain.
Each block of this data contains, in addition to the production data, a unique identification called the 'Hash' and the 'Hash' of the block before it, which identifies another part of this same GxP data.
The blockchain of a data is then formed by this 'hash' identification of the block itself and the block prior to it.
When any unauthorized alteration or attempted manipulation occurs in one of the blocks in this chain, the Hash number is changed. Consequently, all points in this network that have access to these transactions will cause inconsistency of the improper alteration and it will not validate this new information entered.
If the data entered is not validated, it will not be part of this block chain causing hash tag non-receipt needed to link it to the other data blocks.
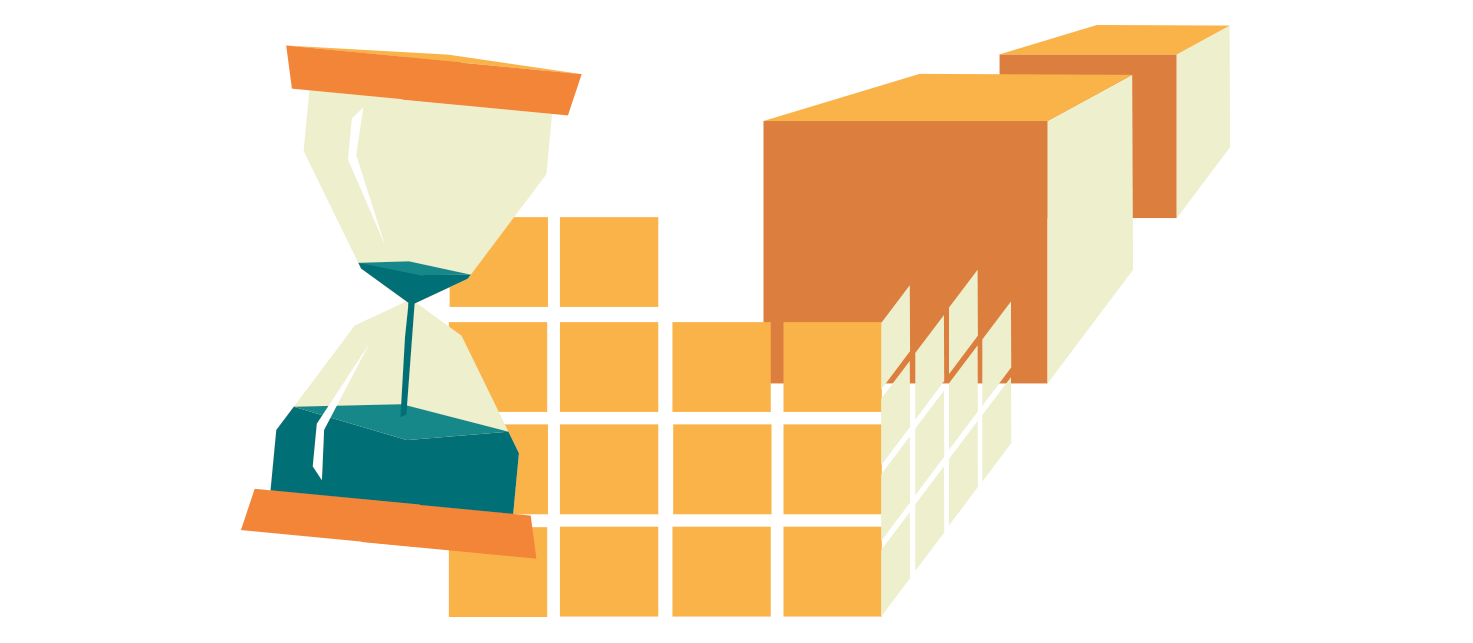
Proof-to-work (PoW)
Another tool to prevent improper access and change of data blocks is proof-to-work. A blockchain condition in which to create a new data block must wait X minutes (i.e. 10 minutes for Blockchain). Thus, in case of an external attack on the data of one of the blocks, it would be necessary to recreate the following blocks to redo the hash numbers so that they can be identified, and the attack is not noticed. But thanks to proof-to-work, there is no time for it.
Another tool to prevent improper access and change of data blocks is proof-to-work. A blockchain condition in which to create a new data block must wait X minutes (i.e. 10 minutes for Blockchain). Thus, in case of an external attack on the data of one of the blocks, it would be necessary to recreate the following blocks to redo the hash numbers so that they can be identified, and the attack is not noticed. But thanks to proof-to-work, there is no time for it.
Audit trails Blockchain structure
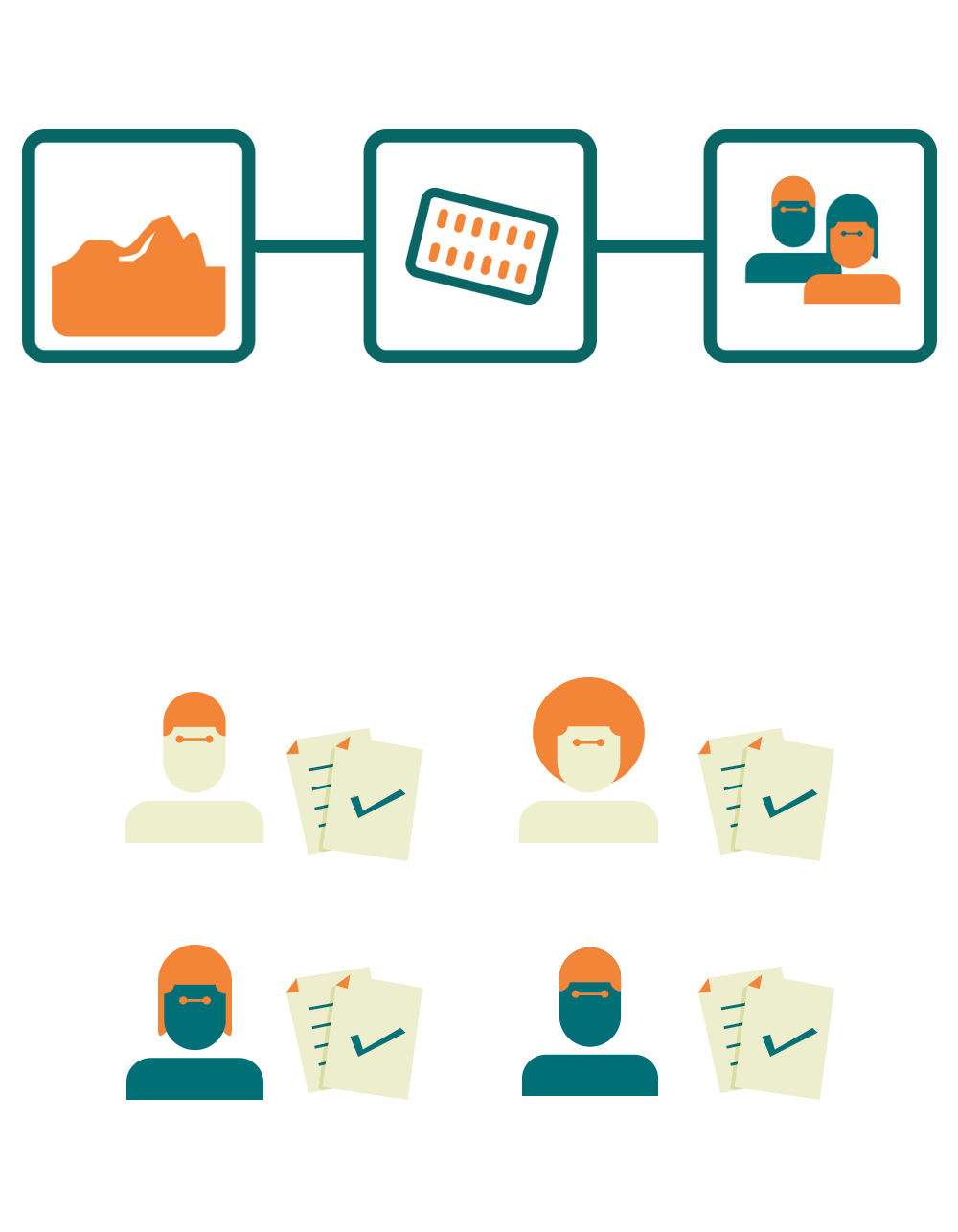
With Blockchain technology, it is possible to record and track all product-related actions across the entire production chain. From raw material to final consumer, everything is recorded with exceptional security and transparency.
Every transaction within the Blockchain structure is given an ID just like the previous transaction. So, it is possible to do the entire reverse path of actions related to a particular batch of medicines, for example.
Any occurrence related to a data block, such as who accessed, who made the change, where and when has to be automatically recorded in the system.
The technology also allows us to create data access controls through access profiles that determine permissions and restrictions.Transparency
All devices involved in manipulating a data within the Blockchain structure have access to actions regarding that data, but the technology also allows us to omit some information from the participants of this structure, in case of confidential data.
Every action regarding a data is written with an encrypted code with all the details of that action and each participating device of this Blockchain structure keeps a copy of these actions.
Transparency and consent from everyone in the structure is combined to give truth to the data and related actions.
In Blockchain, stored data is immutable and permanent, it cannot be modified or deleted, which makes the technology meet the main data integrity requirements, according to the FDA's ALCOA concept.
Every transaction within the Blockchain structure is given an ID just like the previous transaction. So, it is possible to do the entire reverse path of actions related to a particular batch of medicines, for example.
Any occurrence related to a data block, such as who accessed, who made the change, where and when has to be automatically recorded in the system.
The technology also allows us to create data access controls through access profiles that determine permissions and restrictions.Transparency
All devices involved in manipulating a data within the Blockchain structure have access to actions regarding that data, but the technology also allows us to omit some information from the participants of this structure, in case of confidential data.
Every action regarding a data is written with an encrypted code with all the details of that action and each participating device of this Blockchain structure keeps a copy of these actions.
Transparency and consent from everyone in the structure is combined to give truth to the data and related actions.
In Blockchain, stored data is immutable and permanent, it cannot be modified or deleted, which makes the technology meet the main data integrity requirements, according to the FDA's ALCOA concept.
Blockchain and PDF document security
Blockchain has features that can help address some data security issues in PDF documents, such as versioning edited documents, certifying that different versions of the same file remain identical, and inability to review and sign them in parallel.
When a PDF document is inserted into the Blockchain, the original version of this document is given a hash number, stored in a data block, and distributed to all parts of that structure in the Blockchain. The different parties who have access to this file can verify the integrity of this PDF by comparing the hash number they received with the hash stored in the Blockchain.
In addition, when there are multiple copies of the document, such as contracts that require different signatures, you can also track the sequence of actions performed on the document by looking at the change records recorded in the file metadata. This also makes it possible to make sure that the document is in the latest version and the copies distributed between different parts are identical.
As we see, Blockchain features related to information security will also find different uses and solutions to common business problems.
Referências:
https://www.blockchain.com
https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidances/ucm495891.pdf
How does a blockchain work? - Simply Explained
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SSo_EIwHSd4&t=5s
*Article written by Demetrius Rocha with the contribution of Rafael Almeida and reviewed by Silvia Martins
When a PDF document is inserted into the Blockchain, the original version of this document is given a hash number, stored in a data block, and distributed to all parts of that structure in the Blockchain. The different parties who have access to this file can verify the integrity of this PDF by comparing the hash number they received with the hash stored in the Blockchain.
In addition, when there are multiple copies of the document, such as contracts that require different signatures, you can also track the sequence of actions performed on the document by looking at the change records recorded in the file metadata. This also makes it possible to make sure that the document is in the latest version and the copies distributed between different parts are identical.
As we see, Blockchain features related to information security will also find different uses and solutions to common business problems.
Referências:
https://www.blockchain.com
https://www.fda.gov/downloads/drugs/guidances/ucm495891.pdf
How does a blockchain work? - Simply Explained
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SSo_EIwHSd4&t=5s
*Article written by Demetrius Rocha with the contribution of Rafael Almeida and reviewed by Silvia Martins




